
In horizontal analysis, the changes in specific financial statement values are expressed as a percentage and in U.S. dollars. To calculate the percentage change, first select the base year and comparison year. Subsequently, calculate the dollar change by subtracting the value in the base year from that in the comparison year and divide by the base year.
No-BS Guide To Horizontal Analysis – Formulas And Examples
While horizontal analysis is primarily used for financial data, it can also be applied to non-financial data to identify trends and patterns. To further illustrate Car Dealership Accounting the practical application of horizontal analysis, let’s explore a few more examples that showcase its effectiveness in assessing financial performance and identifying trends. Analyze the financial statements of key competitors to gain a broader understanding of industry dynamics and identify areas for improvement or potential competitive advantages. Start by choosing the financial statements that are relevant to your analysis objectives. Consider which statements provide the most meaningful insights based on your analysis goals. Horizontal analysis may be conducted for balance sheet, income statement, schedules of current and fixed assets and statement of retained earnings.
Collect Data
By its nature, horizontal analysis is useful to forecast future performance by analyzing how key metrics change over time. Comparing data across periods makes it easier to identify trends for future projections. Horizontal analysis is an essential tool for making sense of financial trends.
- With horizontal analysis, companies can simulate how rising costs or economic downturns affect future performance.
- According to the variance, the financial impact was advantageous due to the rise in revenue.
- It helps identify recurring patterns and assess the long-term performance of the company.
- Both years are compared with each other and it can be seen generally that there has been a significant increase in earning from all sources.
- Given below is a horizontal analysis in excel of a comparative income statement (i.e. year 1 – base, year 2, and year 3).
- Here, for the sake of illustration, we have shown the absolute change (in US$) and percentage change (%) of all line items in the income statement between year 1 and year 2 only.
- Per usual, the importance of completing sufficient industry research cannot be overstated here.
Understanding Horizontal Analysis

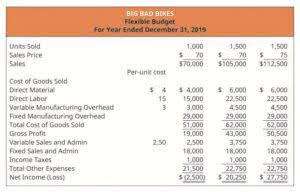
Comparing costs like COGS and operating expenses across periods and finding what could be more efficient gross vs net is also a common use case for horizontal analysis. A manufacturer might notice that its expenses are rising faster than its sales, and closely look at cost control. Let us assume that we are provided with the income statement data of ABC Co. We need to perform a horizontal analysis of the income statement of this company.
- In this first example, I will be doing a horizontal analysis of Company A’s revenue based on its annual income statement.
- There are two primary methods for analysing trends from horizontal analysis.
- Other factors must be considered in order to interpret the significance of adjustments in either direction.
- For this, we compare the absolute change ($) and percentage change (%) in all the line items from one period to the other.
- From this, it is seen that, for instance, with vertical analysis, every item on an income statement is expressed as a percentage of the gross sales.
- In order to calculate the absolute change, subtract the figure from the earlier period from the figure from the later period.
The Financial Modeling Certification

By examining the historical data and calculating percentage changes, horizontal analysis helps in understanding the direction and magnitude of changes, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning. To conduct horizontal analysis i.e. evaluate underlying trends, it’s essential to compare financial statements of a company or companies over two or more accounting periods. Income statements and balance sheets are the primary financial statements that are necessary for horizontal analysis.
Key Objectives and Purposes:
The year of comparison for horizontal analysis is analysed for dollar and percent changes against the base horizontal analysis formula year. Horizontal analysis is a powerful tool for understanding and evaluating a company’s financial performance over time. By examining year-to-year changes in key financial metrics, you can identify trends, assess stability, and make informed business decisions. Remember to consider industry benchmarks, peer analysis, and best practices to ensure accurate and meaningful results. By incorporating horizontal analysis into your financial analysis toolkit, you can gain valuable insights into your company’s performance and drive strategic growth.
Trial Balance

It means the changes are shown as a percentage of a base item in the statement and there are no representations for variance. Financial statement analysis presents you with your firm’s liquidity, debt, and profitability, emerging problems, and strengths. All these are taken into account in relation to identifying your past financial performance and your prospects for the future. The final step involves you reviewing these changes and making appropriate use of the information you get from your analysis.
Horizontal Analysis Examples
Each period is compared to a year you choose as a baseline to see how revenue, expenses or profits have evolved. If the comparison year is year 3, then we will input the net income of year 3 and compute the percentage change between year 3 and year 1 (base year). To illustrate, consider an investor who wishes to determine Company ABC’s performance over the past year before investing. Assume that ABC reported a net income of $15 million in the base year, and total earnings of $65 million were retained.
